Eine umfassende Übersicht darüber, wie VNS-Geräte die autonome Funktion wiederherstellen, indem sie Dysregulationen des Nervensystems angehen—mit Expertenrankings der vier besten zertifizierten Optionen.

Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is estimated to affect between 1 and 3 million people in the United States, causing debilitating symptoms when transitioning from lying to standing. Unlike simple dehydration or deconditioning, Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities reflects a fundamental dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system dysfunction, disrupting cardiovascular regulation, blood flow distribution, and cellular energy metabolism.
Recent neuroscience research suggests that vagus nerve dysfunction may be an important contributing mechanism in a subset of Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities individuals, alongside hypovolemia, peripheral neuropathy, hyperadrenergic states, and autoimmune processes. When this principal parasympathetic nerve demonstrates reduced activity, the body may lose some capacity to modulate heart rate appropriately, maintain cerebral perfusion, and regulate peripheral vascular tone.
This guide examines the relationship between vagus nerve function and Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities symptomatology and evaluates the leading vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) devices that may help restore autonomic balance and functional capacity.
Symptoms of Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities
Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities are characterised by an excessive increase in heart rate (≥30 bpm in adults, ≥40 bpm in adolescents) within 10 minutes of standing, without orthostatic hypotension. Common manifestations include:
Kardiovaskuläre Symptome:
- Herzfrequenzerhöhung über 120 Schläge pro Minute beim Stehen
- Herzklopfen oder Gefühl eines schnellen, kräftigen Herzschlags
- Beschwerden oder Druck in der Brust
- Peripheral vascular dysregulation (venous pooling, cold extremities, colour changes)
- Präsynkope (Benommenheit, Ohnmachtsanfälle)
- Synkope (tatsächlicher Bewusstseinsverlust)
Zerebrovaskuläre Symptome:
- Cognitive impairment ("brain fog"), particularly when upright
- Sehstörungen (Tunnelblick, verschwommenes Sehen, Sichtschnee)
- Difficulty with concentration and information processing while upright
- Probleme bei der Speicherkonsolidierung
- Kopfschmerzen (oft orthostatischer Natur)
Autonome Dysregulation:
- Temperaturdysregulation (Hitzeintoleranz, unangemessenes Schwitzen)
- Gastrointestinal dysmotility (nausea, early satiety, constipation, diarrhoea)
- Häufiges oder dringendes Wasserlassen
- Zittern oder inneres Zittern
- Belastungsintoleranz mit verlängerten Erholungsphasen
Systemische Symptome:
- Starke Müdigkeit, die nichts mit dem Belastungsniveau zu tun hat
- Störung der Schlafarchitektur
- Anxious thoughts (often secondary to physical symptoms)
- Muskelschwäche oder Schmerzen
- Post-Exertional Malaise, die 24-48 Stunden anhält
Die funktionellen Auswirkungen gehen über die Symptomatologie hinaus: Unfähigkeit, eine Beschäftigung aufrechtzuerhalten, Bildungsstörungen, soziale Isolation, Verlust der Unabhängigkeit und erhebliche Verringerung der Lebensqualitätskennzahlen.

Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities Self-Assessment
Bewerten Sie die Symptome, die Sie regelmäßig erleben:
Herz-Kreislauf-Funktion
- Herzfrequenz steigt ≥30 Schläge pro Minute innerhalb von 10 Minuten nach dem Stehen
- Herzklopfen oder schneller Herzschlag im aufrechten Zustand
- Benommenheit oder Beinahe-Ohnmacht beim Stehen
- Kalte Hände und Füße trotz ausreichender Umgebungstemperatur
- Brustbeschwerden beim Aufrichten
Zerebrovaskuläre Funktion
- Gehirnnebel oder kognitive Verlangsamung im Stehenv
- Sehstörungen (Dimmen, Tunnelblick, Mouches volantes)
- Difficulty maintaining concentration in the upright position
- Kopfschmerzen, die sich im Liegen bessern
- Gedächtnisprobleme, die die tägliche Funktion beeinträchtigen
Postural Tolerance
- Must sit or lie down frequently throughout the day
- Kann nicht länger als 10-15 Minuten stehen
- Die Symptome verschlimmern sich in warmen Umgebungen
- Morning symptoms are particularly severe
- Duschen oder Baden löst eine Verschlimmerung der Symptome aus
autonome Symptome
- Gastrointestinale Probleme (Übelkeit, Blähungen, veränderte Motilität)
- Schwierigkeiten bei der Temperaturregulierung
- Übermäßiges oder unzureichendes Schwitzen
- Zittern oder Zittern
- Schlafstörungen trotz Müdigkeit
Funktionsfähigkeit
- Unfähig, Vollzeit zu arbeiten oder die Schule zu besuchen
- Exercise causes a multi-day symptom flare
- Muss Aktivitäten rund um das Symptommanagement planen
- Erhebliche Änderungen des Lebensstils erforderlich
- Normale Blutdruckwerte trotz Symptomen
Diagnostische Vorgeschichte
- Symptoms began after a viral illness, pregnancy, surgery, or trauma
- Der Kipptischtest bestätigte einen übermäßigen Anstieg der Herzfrequenz
- The cardiologist ruled out primary cardiac pathology
- Standardmäßige autonome Tests zeigen Anomalien
- Konventionelle Interventionen bieten unvollständige Linderung
If you identify with multiple features across the cardiovascular, postural tolerance, and autonomic categories, Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities may be a consideration and warrant formal evaluation by a clinician experienced in autonomic disorders.
In some individuals, impaired vagal tone and parasympathetic withdrawal may contribute to symptom severity, making therapies that support autonomic regulation a potential adjunct, under medical guidance.
Die Stimulation des Vagusnervs kann als zusätzlicher Ansatz ein Gespräch mit Ihrem Arzt rechtfertigen.
Die Vagusnervverbindung
Was ist der Vagusnerv?
Der Vagusnerv (Hirnnerv X) ist der längste und komplexeste Nerv des autonomen Nervensystems. Er entspringt in der Medulla oblongata und ragt durch den Hals, um Herz, Lunge und Magen-Darm-Trakt zu innervieren. Es vermittelt kritische homöostatische Funktionen:
- Kardiovaskuläre Regulation (chronotrope und dromotrope Modulation)
- Erzeugung von Atmungsmustern
- Gastrointestinale Motilität und Sekretion
- Entzündungsreflexweg (cholinerger entzündungshemmender Weg)
- Barorezeptor-Reflexintegration
- Stoffwechselregulation
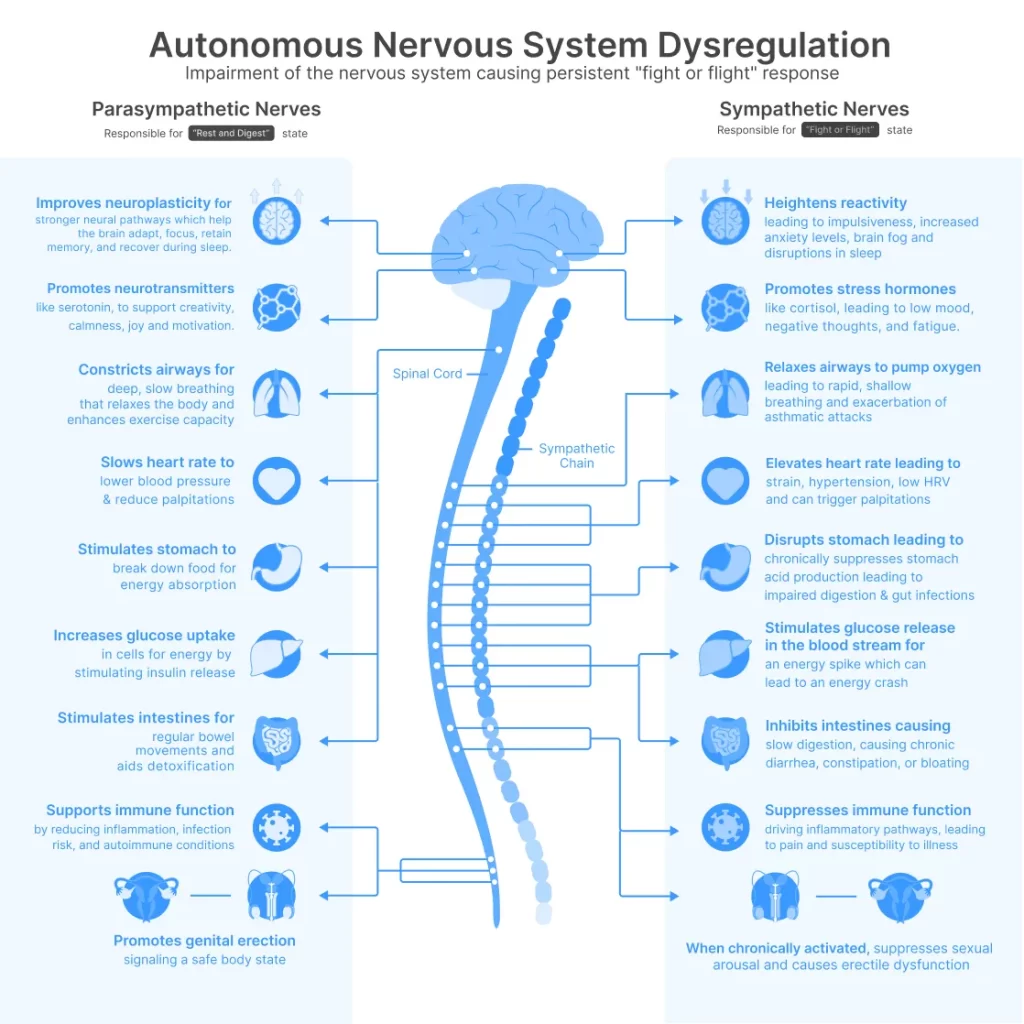
Das Zwei-Modus-System
Ihr autonomes Nervensystem funktioniert über zwei komplementäre Abteilungen:
- Sympathisch (thorakolumbaler Ausfluss): Increases heart rate, elevates blood pressure, mobilises glucose, redistributes blood flow to skeletal muscle—activated during stress or perceived threat.
- Parasympathikus (vagaler Ausfluss): Controlled predominantly by the vagus nerve, reduces heart rate, promotes digestion, facilitates recovery, supports cellular restoration and repair mechanisms.
Healthy autonomic function requires a dynamic balance between these systems, with rapid shifts based on postural demands, environmental context, and metabolic requirements. However, infection, autoimmune activation, or sustained stress can impair vagal tone, creating sympathetic predominance.
How Vagus Nerve Dysfunction Causes Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities
Wenn Ihr Vagusnerv eine verringerte Aktivität aufweist (niedriger Vagustonus):
- Kardiovaskuläre Dysregulation: Loss of parasympathetic counterbalance to sympathetic activation causes excessive heart rate acceleration upon standing. Without appropriate vagal braking, a rapid heartbeat becomes the primary compensatory mechanism for maintaining cardiac output and cerebral perfusion.
- Beeinträchtigte Barorezeptorempfindlichkeit: The vagus nerve transmits arterial baroreceptor signals to the brainstem cardiovascular centres. Dysfunction impairs this feedback loop, preventing appropriate blood pressure and heart rate adjustments during postural changes.
- Periphere Gefäßanomalien: Reduced vagal activity contributes to inadequate vasoconstriction in the lower extremities, allowing venous pooling. As much as 500–800 mL of blood may pool in the lower extremities and splanchnic circulation upon standing, reducing venous return and triggering compensatory rapid heartbeat.
- Reduzierte Herzfrequenzvariabilität (HRV): HRV serves as a validated biomarker of vagal tone. Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities individuals consistently demonstrate markedly reduced HRV, indicating parasympathetic withdrawal and reduced capacity for cardiovascular adaptation.
- Chronische sympathische Aktivierung: Compensatory sympathetic overdrive maintains elevated norepinephrine levels (often 2-3x normal when standing), causing tremor, anxious thoughts, sweating, and progressive receptor desensitisation—worsening symptoms over time.
- Entzündliche Dysregulation: Der Vagusnerv steuert den cholinergen entzündungshemmenden Weg. Eine Funktionsstörung ermöglicht eine chronische, leichte Entzündung, die die Endothelfunktion, die mitochondriale Effizienz und die zelluläre Energieproduktion direkt beeinträchtigt —was zu Müdigkeit und Belastungsintoleranz beiträgt.
It is important to note that Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities is a heterogeneous syndrome rather than a single disease entity. Vagus nerve dysfunction does not account for all cases. Some individuals exhibit predominant hypovolemia, others neuropathic or hyperadrenergic features, and many demonstrate overlapping mechanisms. Vagal impairment appears most relevant in individuals with reduced heart rate variability, autoimmune markers, or post-viral onset.

die wissenschaftlichen Beweise
Published research establishes clear relationships between vagus nerve dysfunction and Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities pathophysiology:
- Profil der autonomen Funktionsstörung: Studies document that Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities individuals exhibit distinct autonomic abnormalities consistent with impaired vagal and sympathetic cardiovascular control, including decreased vagal baroreflex sensitivity and impaired sympathetic responsiveness. Heart rate variability parameters—validated biomarkers of vagal tone—are markedly reduced compared to healthy controls.
- Autoimmunmechanismen: Growing evidence indicates Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities may represent an autoimmune disorder. Research demonstrates increased expression of autoantibodies against adrenergic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities individuals. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor (α-1 AR) autoantibodies are significantly elevated in most individuals with Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities, with a subset of individuals (approximately 20–30% in some cohorts) showing elevated α1-AR and α2-AR antibodies. These adrenergic receptor autoantibodies correlate significantly with orthostatic intolerance severity—a cardinal Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities feature.
- Scientific trial evidence for vagus nerve stimulation: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled scientific trial conducted at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center (led by Associate Professor Stavros Stavrakis) demonstrated scientifically meaningful improvements in orthostatic rapid heartbeat associated with transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation for Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities:
- Studiendesign: 26 Teilnehmer (aktiv n=12, Placebo n=14) erhielten 2 Monate lang täglich eine Stunde Stimulation mittels aurikulärer Vagusnervstimulationstechnologie
- Primärziel: Postural rapid heartbeat was significantly reduced in the active group versus the placebo. Postural heart rate increase was 18±10 bpm in the therapy group compared to 32±14 bpm in the placebo (p=0.016)—representing a scientifically meaningful 14 bpm difference.
- Mechanistische Erkenntnisse: Anti-autonomic autoantibodies were significantly lower in the therapy group after 2 months compared to placebo, providing mechanistic insight into Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities pathophysiology
- Sicherheitsprofil: Es wurden keine gerätebedingten Nebenwirkungen gemeldet; alle Probanden zeigten eine ausgezeichnete Einhaltung des Protokolls
- Beweisklassifizierung: This represents Level IB evidence according to the Center for Evidence-Based Medicine recommendations—providing strong support for scientific application
- Post-viral Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities connection: Post-viral syndromes, including Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities following SARS-CoV-2 infection, demonstrate marked vagal impairment and elevated inflammatory markers that are normally regulated by vagal anti-inflammatory pathways. Studies indicate that a small but scientifically significant proportion of individuals recovering from SARS-CoV-2 infection develop Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities or Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities-like autonomic dysfunction, particularly following moderate to severe illness.
- Die mechanistische Schlussfolgerung: Restoring vagus nerve function through targeted stimulation addresses the underlying autonomic and immunological pathophysiology of Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities—including both parasympathetic withdrawal and autoantibody-mediated dysfunction—rather than merely suppressing symptoms.
VNS-Geräte als Lösung: So funktionieren sie
Der technologischen Revolution
Until recently, vagus nerve stimulation required invasive surgical procedures—implanting electrodes directly on the nerve through operations that carried surgical risks, recovery time, and permanent device placement. This confined VNS therapy primarily to therapy- beständige cases of depressive states where the benefits justified surgical intervention.
Der heutige Durchbruch verändert alles.
Die moderne transkutane Vagusnervstimulation (tVNS) liefert die gleichen therapeutischen elektrischen Impulse an den Vagusnerv —erleichtert die neuroplastische Anpassung und Wiederherstellung eines geeigneten Tonus—, jedoch völlig nicht-invasiv durch die Haut. Keine Operation. Keine Implantation. Keine Erholungsphase.
Diese fortschrittlichen Geräte erreichen eine bemerkenswerte Wirksamkeit mit einem außergewöhnlichen Sicherheitsprofil und arbeiten über präzise positionierte Elektroden an zwei zugänglichen Stellen:
- Zervikal (Hals): Targeting the cervical branch of the vagus nerve near the carotid artery, where the nerve courses superficially beneath the skin
- Ohrmuschel (Ohr): Ziel ist der Ohrast des Vagusnervs, der den Tragus und die Cymba conchae innerviert —der einzige Ort, an dem Hirnnerven die Körperoberfläche erreichen
This represents a fundamental shift: vagus nerve stimulation therapy that was once confined to operating rooms is now available for daily home use, with wissenschaftlich-grade precision and zero surgical risk.
Wirkmechanismus
Wenn präzise kalibrierte elektrische Impulse den Vagusnerv erreichen, lösen sie eine Kaskade neurophysiologischer Reaktionen aus:
- Neurotransmittermodulation: Die Stimulation löst die Freisetzung von Acetylcholin an parasympathischen Enden aus, wirkt der sympathischen Dominanz direkt entgegen und aktiviert cholinerge entzündungshemmende Wege
- Aktivierung des Hirnstammkerns: Afferent vagal signals project to the nucleus tractus solitarius, which integrates autonomic regulatory information and modulates cardiovascular control Kompetenzzentren in the medulla
- Autonome Neuausrichtung: Consistent stimulation protocols facilitate a shift from sympathetic dominance toward parasympathetic restoration, improving heart rate variability and baroreflex sensitivity
- Verbesserung der Neuroplastizität: VNS promotes synaptic reorganisation in central autonomic networks, potentially restoring normal cardiovascular regulatory capacity
- Entzündungshemmung: Die vagale Stimulation aktiviert den cholinergen entzündungshemmenden Weg und reduziert die Produktion entzündungsfördernder Zytokine (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6), was zur endothelialen Dysfunktion und zur Aufrechterhaltung der Symptome beiträgt
klinischen Parameter
Forschungsvalidierte VNS-Protokolle verwenden typischerweise:
- Sitzungsdauer: 30–60 Minuten täglich (unter Berücksichtigung anhaltender neurophysiologischer Effekte)
- Intensität: Individualised to sensory threshold (perceptible but comfortable stimulation)
- Konsistenz: Daily application for a minimum of 8-12 weeks (neuroplastic changes require sustained intervention)
erwarteten Zeitplan
VNS fördert eher eine allmähliche Anpassung des Nervensystems als eine sofortige Symptomunterdrückung:
- Woche 1–2: Verstärkte Entspannungsreaktion während Stimulationssitzungen, leichte Verbesserungen der Schlafarchitektur, mögliche leichte Verringerung der Ruheherzfrequenz
- Woche 3–4: Noticeable improvements in orthostatic tolerance, reduced rapid heartbeat intensity, decreased presyncope frequency, improved cognitive function when upright
- Monat 2–3: Anhaltende kardiovaskuläre Stabilität, erhöhte Stehtoleranz, verringerte Symptomschwere, messbare HRV-Verbesserungen, geringere Abhängigkeit von Symptommanagementstrategien
- Monat 3+: Wiederherstellung des autonomen Gleichgewichts, Verbesserung der funktionellen Kapazität, Fähigkeit zur Wiederaufnahme bisher eingeschränkter Aktivitäten, verbesserte Lebensqualität
Sicherheitserwägungen
VNS using transcutaneous approaches is generally well-tolerated in scientific research. Potential transient responses may include:
- Mild tingling sensation at the stimulation site
- Temporary muscle tension in the neck region (cervical devices)
- Kurze Benommenheit (löst sich normalerweise durch Protokollanpassung auf)
Wichtige Einschränkungen: Not appropriate for individuals with cardiac pacemakers, recent acute cardiac events, pregnancy, or a history of vagotomy. Healthcare provider consultation is essential prior to initiating any VNS protocol.
Top 4 VNS Devices for Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities
#1: Nurosym
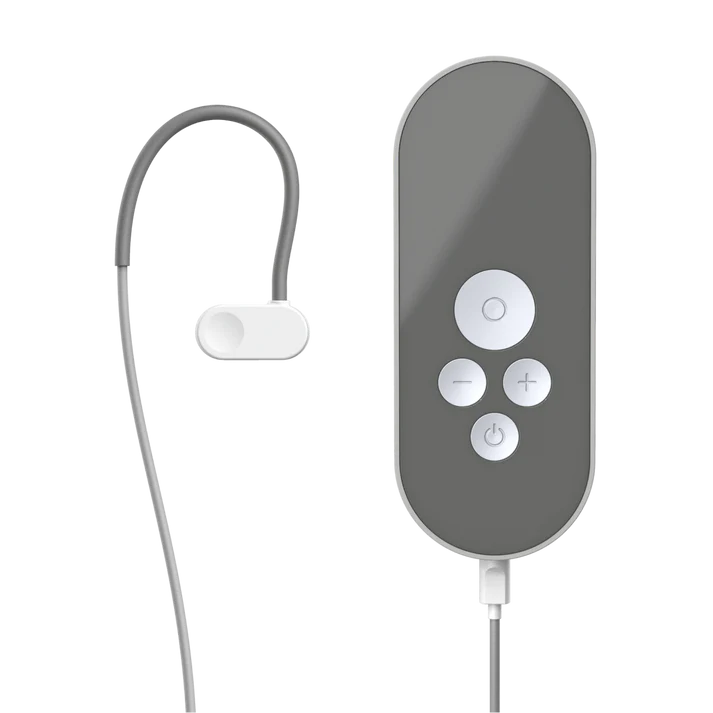

Preis: 700 EUR Varies by region (€40 research subsidy available)
Art: Ohrmuschel (am Ohr getragen)
Bleifreitechnologie: AVNT™ von Parasym
Warum Nr. 1:
- Am umfassendsten validiert: Supported by 50+ peer-reviewed publications from Harvard Medical School, UCLA, and leading research institutions worldwide.
- Nachgewiesene Wirksamkeit bei autonomer Dysfunktion: Scientific studies document 61% improvement in vagal tone (HRV metrics), significant reduction in sympathetic overactivation, and improved cardiovascular regulation.
- Unabhängige Zertifizierung: CE-marked wearable device meeting rigorous safety and performance standards—third-party verified.
- Scientific adoption: Used by 1000+ healthcare professionals and researchers; integrated into institutional protocols; 4,000,000+ supervised stimulation sessions completed.
- Evidenzbasierte Parameter: Stimulation protocols derived from peer-reviewed research, not proprietary guesswork.
- Umfassende Unterstützung: 30-day evaluation period, scientific guidance resources, responsive technical support.
Empfohlen für: Individuals seeking the most scientifically validated device, particularly those with autonomic dysfunction (Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities, dysautonomia), post-viral syndromes, or those prioritising evidence over marketing claims.
#2: Truvaga Plus
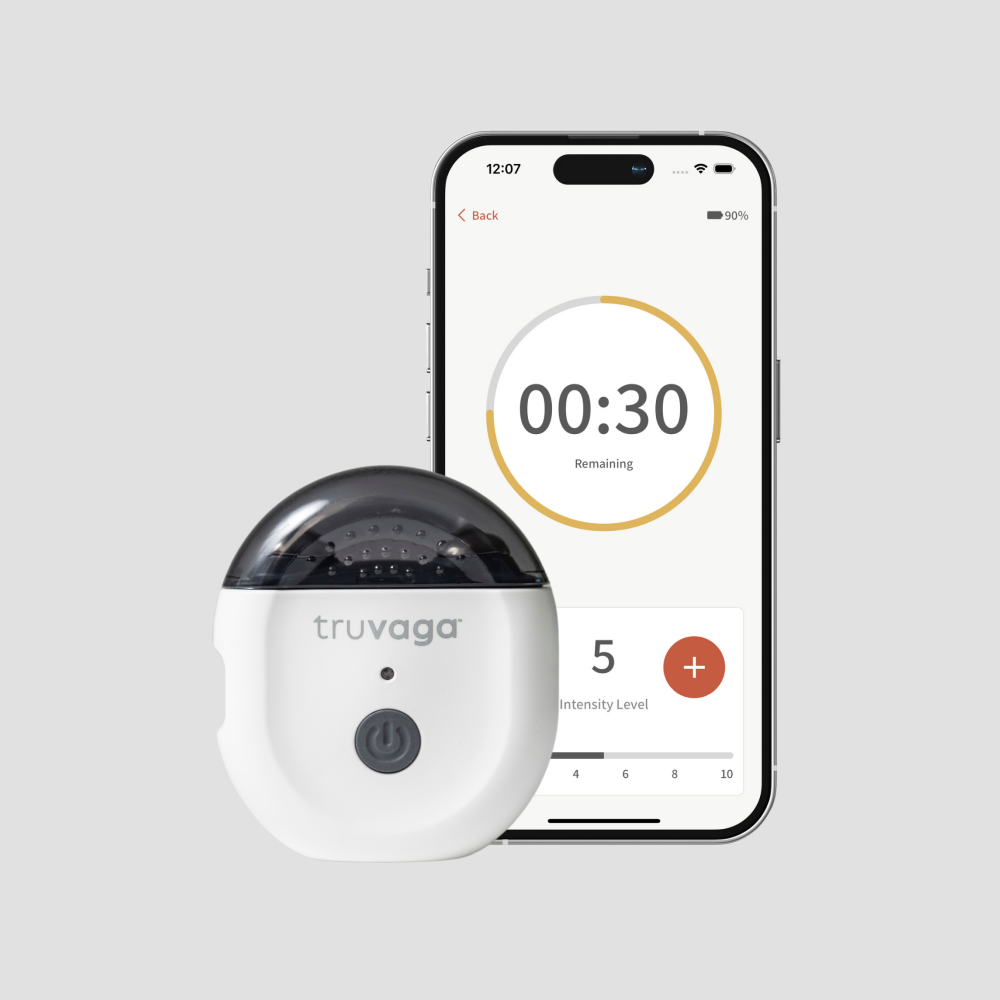

Preis: 544 $+ (Gerät 499 $ + Spray 45 $/Jahr + mögliches Abonnement) Typ: Halswirbelsäule (Handgerät für den Hals)
Technical note: Shares core technology with gammaCore, an FDA-cleared device for migraine/cluster headache (not Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities). Rapid parasympathetic effects. Straightforward protocol.
Überlegungen: Ongoing costs for conductive spray plus potential app subscription—verify pricing before purchase. Common adverse effects include muscle spasms, facial droop, lip pull, and headache. Not suitable for users with cardiac states, pacemakers, or recent heart issues. Mobile app connectivity problems reported.
Empfohlen für: Those preferring cervical stimulation with FDA-cleared technology lineage (for migraine, not Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities) who can tolerate potential facial muscle spasm adverse effects.
#3: Pulsetto

Preis: 350–371 $ (Gerät 269 $ + Gel 81–102 $/Jahr) Typ: Halsband (Freihandkragen)
Vorteile: Freihändiges tragbares Design. HSA/FSA-berechtigt. 2 Jahre Garantieschutz.
Kritische Einschränkungen: No peer-reviewed scientific studies demonstrating efficacy for Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities—only company press releases and retail testimonials. Frequent fit problems create inadequate nerve contact, especially with smaller necks. Users consistently report minimal to no improvement in Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities symptoms compared to research-validated devices.
Not recommended for Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities: The $200-350 price difference seems attractive until you calculate the real cost: months of continued disability while using an unproven device. Lower-cost devices may appear attractive; however, the absence of scientific validation means their effectiveness for autonomic disorders like Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities remains uncertain.
#4: Sinnlich
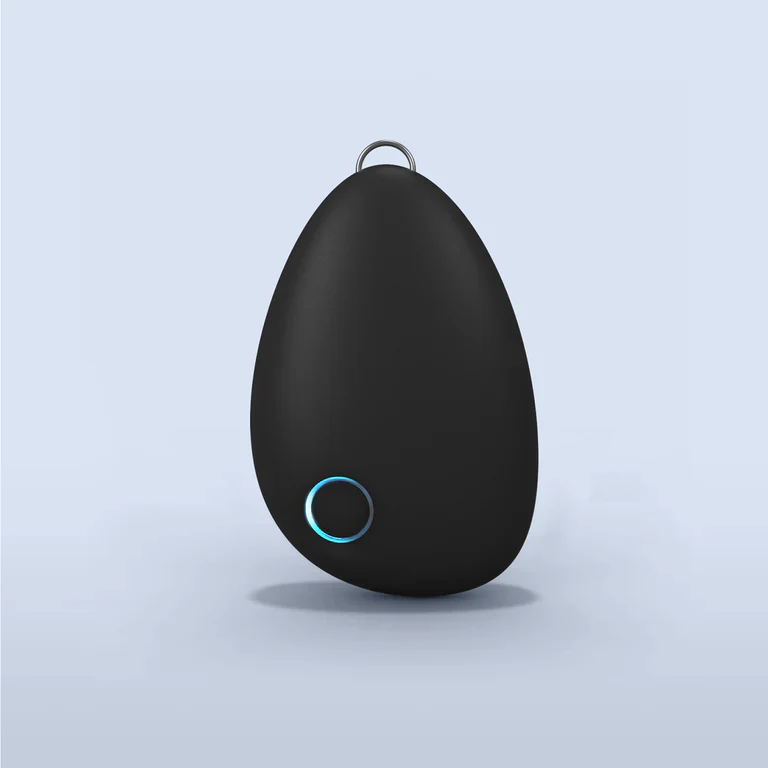

Preis: 299–349 $ Typ: Vibrotaktiles Gerät zum Tragen auf der Brust (kein echtes VNS)
Advantages: Comfortable pebble design worn on the chest. Simple app interface with soundscapes. Lower price point. Can be used while performing other activities with a neck strap.
Kritische Unterscheidung: Sensate does not directly stimulate the vagus nerve through electrical impulses like other devices in this comparison. Instead, it uses infrasonic vibrations and bone conduction placed on the chest—an indirect approach targeting general stress reduction rather than specific vagal nerve activation. While bone conduction at the ear has some research supporting vagal stimulation, Sensate’s chest placement lacks scientific substantiation for direct vagus nerve engagement. The mechanism is fundamentally different: actual VNS devices (like Nurosym, Truvaga, and Pulsetto) deliver calibrated electrical signals directly to accessible vagus nerve branches; Sensate delivers vibrations to your sternum, hoping for downstream effects.
For Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities individuals: This matters significantly. Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities require restoration of measurable autonomic function—improved heart rate variability, reduced orthostatic rapid heartbeat, enhanced baroreflex sensitivity. General relaxation devices may help with stress management, but do not address the underlying vagal dysfunction and autonomic dysregulation driving Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities symptoms. No wissenschaftlich Studien demonstrate Sensate’s efficacy for Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities or autonomic disorders—only company-funded studies showing general stress reduction in healthy volunteers.
Empfohlen für: Those seeking a general relaxation and stress management tool rather than targeted vagus nerve stimulation for autonomic dysfunction. Not recommended for individuals Prioritäten evidence-based Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities therapy.
*With a €70 research subsidy for qualifying participants
**Erfordert ein sorgfältiges Intensitätsmanagement und die Einhaltung des Protokolls
Schlussfolgerung: Nurosym offers the most comprehensive scientific validation, proven efficacy for autonomic dysfunction, including Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities, independent regulatory certification, and optimal balance of research foundation and practical application for those prioritising evidence-based outcomes.
handeln
Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities related to vagus nerve dysfunction represent ein symptom with emerging, adjunctive therapeutic approaches. Your autonomic nervous system possesses the capacity for neuroplastic adaptation and restoration of regulatory function.
With support from 50+ scientific studies, independent CE-marking certification, and 4,000,000+ documented stimulation sessions, Nurosym provides scientifically validated potential for restoring autonomic balance and functional capacity.
This information is provided for educational purposes. VNS devices are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. Individuals with Postural Heart Rate Abnormalities should work with qualified healthcare providers to develop comprehensive management strategies. Always consult your physician before beginning any new intervention.
Quellen
- Stavrakis S, Chakraborty P, Farhat K, Whyte S, Morris L, Zain, et al. Noninvasive Vagus Nerve Stimulation in Postural Tachycardia Syndrome. JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology. 2023 Nov 1;
- Wang Z, Zhu T, Li X, Lai X, Chen M. Tragus Nerve Stimulation Attenuates Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome in Post COVID‐19 Infection. Clinical Cardiology. 2025 Feb 27;48(3).
- Stavrakis S, Cai X, Morris L, Whyte S, Karfonta B, Matlock HG, et al. LB-456640-4 NONINVASIVE VAGUS NERVE STIMULATION IN POSTURAL TACHYCARDIA SYNDROME: A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL. Heart Rhythm. 2023 Jul 1;20(7):1090–0.
- Shiffer D, Rigo S, Minonzio M, Yarsuvat DT, Tobaldini E, Furlan L, et al. Short and long term effects of a two-week transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation in hyperadrenergic postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome: a proof-of-concept trial. European Journal of Internal Medicine [Internet]. 2025 Sep 27;106529. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0953620525004078
Teilen über:

